Patents Directory for Dr. Gary K. Michelson — U.S. Published Patents only
340 patents found - Page 7
| Patent | Abstract |
|---|---|
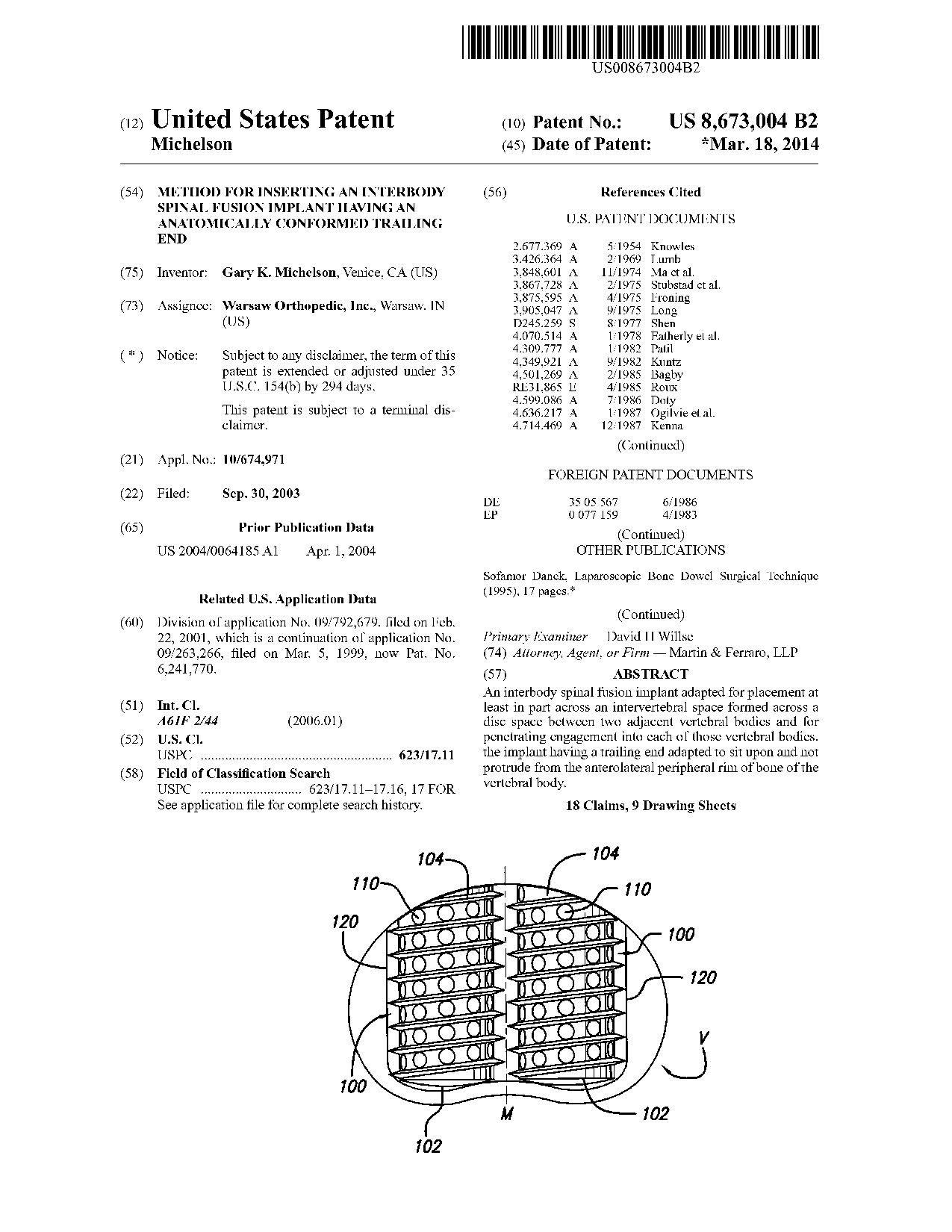 Method for inserting an interbody spinal fusion implant having an anatomically conformed trailing end - Patent 8,673,004 Method for inserting an interbody spinal fusion implant having an anatomically conformed trailing end - Patent 8,673,004
|
An interbody spinal fusion implant adapted for placement at least in part across an intervertebral space formed across a disc space between two adjacent vertebral bodies and for penetrating engagement into each of those vertebral bodies, the implant having a trailing end adapted to sit upon and not protrude from the anterolateral peripheral rim of bone of the vertebral body.
|
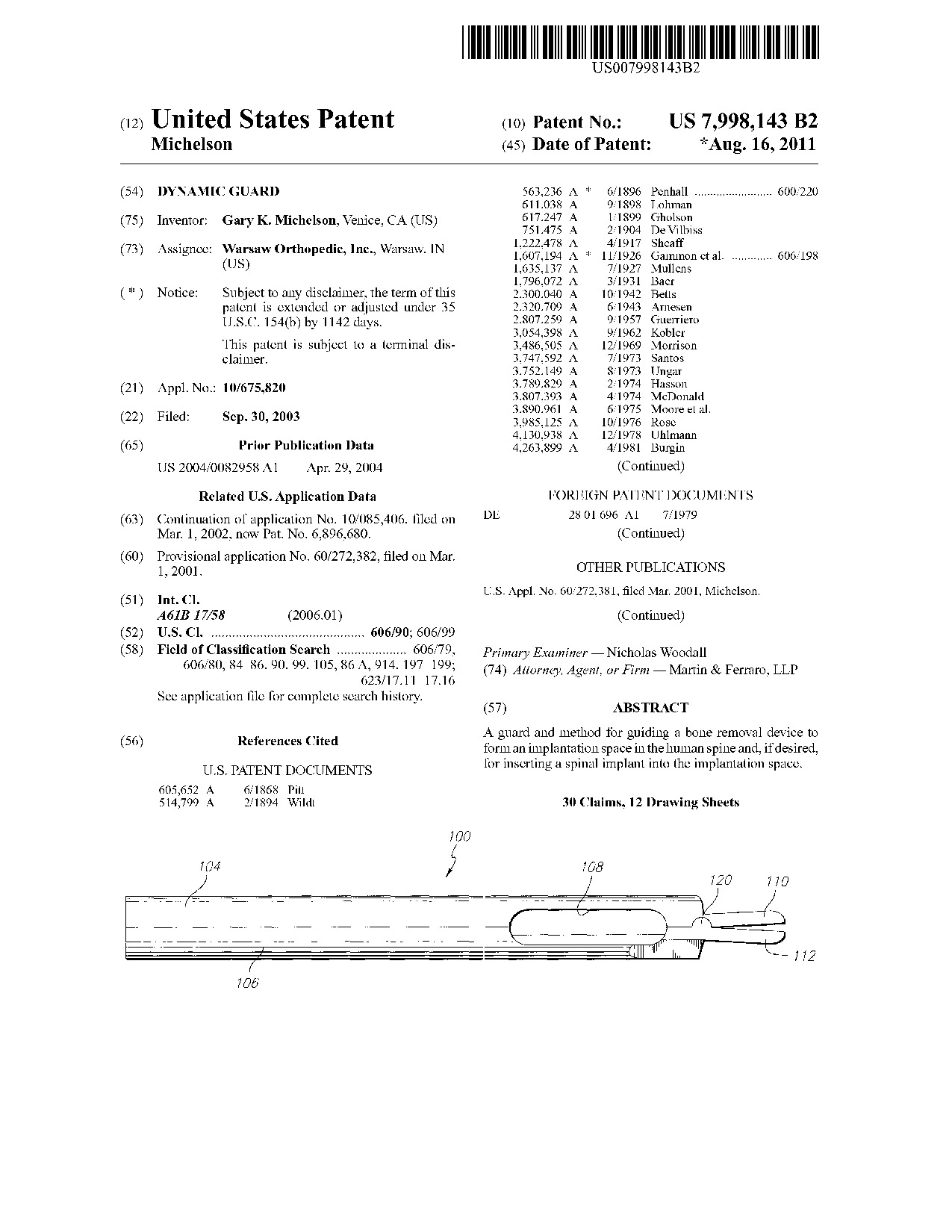 Dynamic guard - Patent 7,998,143 Dynamic guard - Patent 7,998,143
|
A guard and method for guiding a bone removal device to form an implantation space in the human spine and, if desired, for inserting a spinal implant into the implantation space.
|
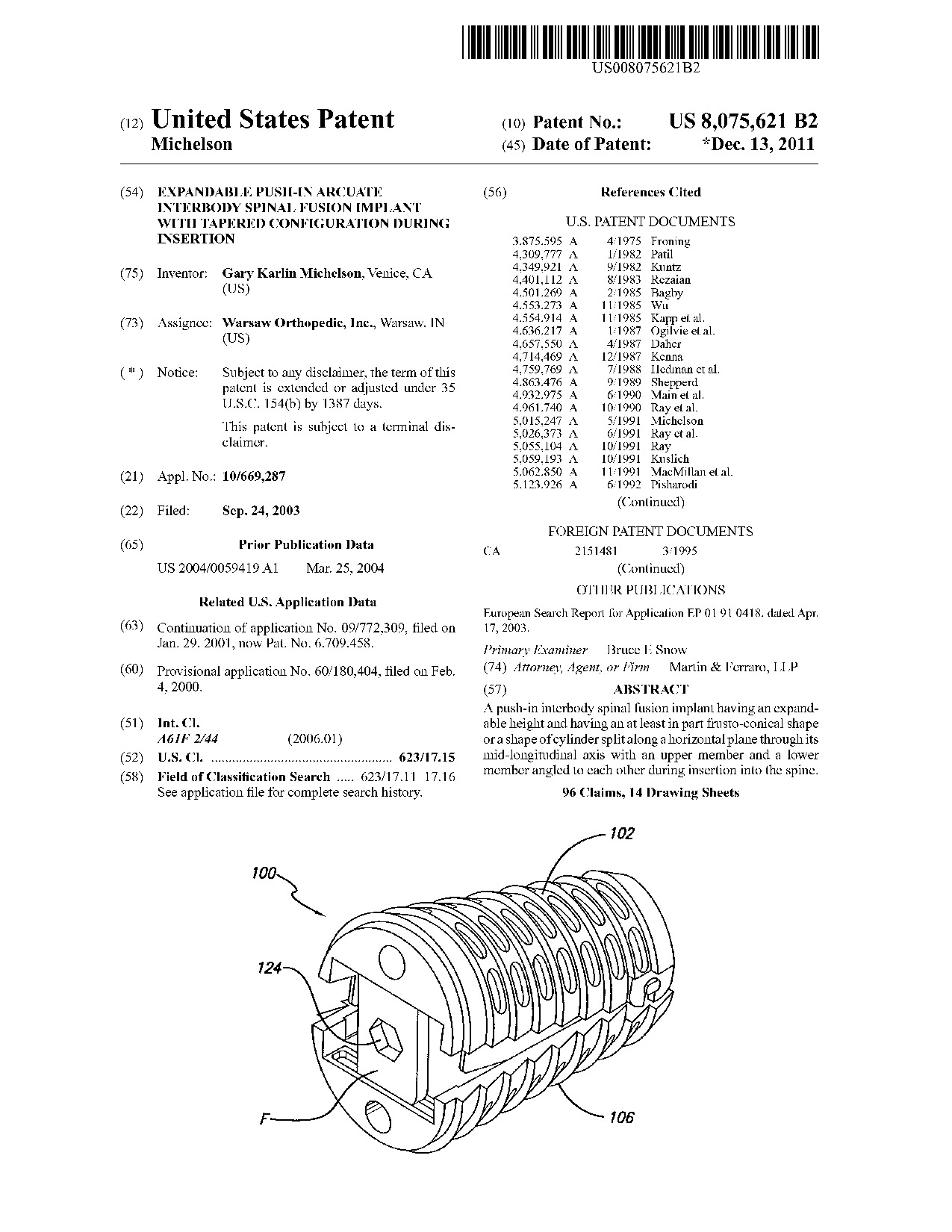 Expandable push-in arcuate interbody spinal fusion implant with tapered configuration during insertion - Patent 8,075,621 Expandable push-in arcuate interbody spinal fusion implant with tapered configuration during insertion - Patent 8,075,621
|
A push-in interbody spinal fusion implant having an expandable height and having an at least in part frusto-conical shape or a shape of cylinder split along a horizontal plane through its mid-longitudinal axis with an upper member and a lower member angled to each other during insertion into the spine.
|
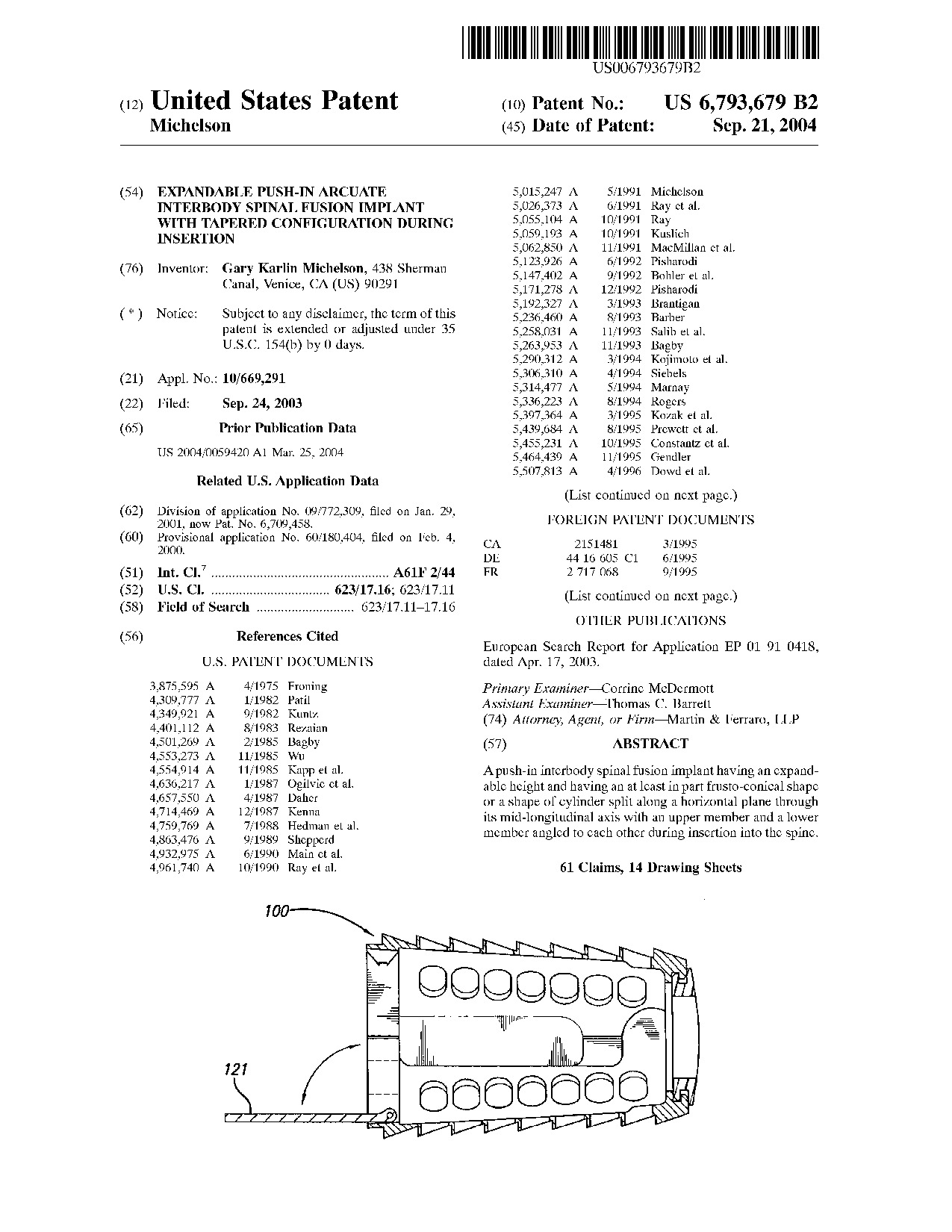 Expandable push-in arcuate interbody spinal fusion implant with tapered configuration during insertion - Patent 6,793,679 Expandable push-in arcuate interbody spinal fusion implant with tapered configuration during insertion - Patent 6,793,679
|
A push-in interbody spinal fusion implant having an expandable height and having an at least in part frusto-conical shape or a shape of cylinder split along a horizontal plane through its mid-longitudinal axis with an upper member and a lower member angled to each other during insertion into the spine.
|
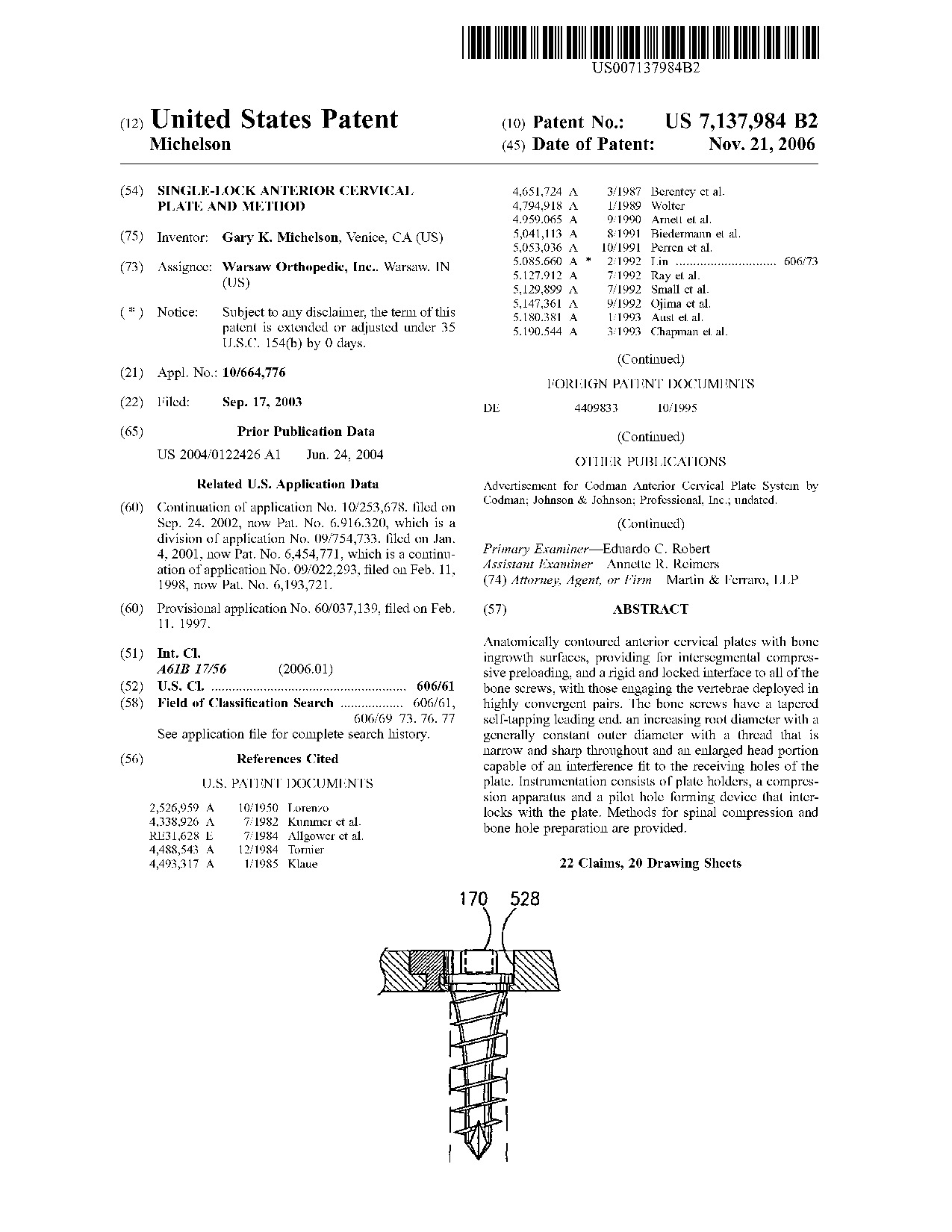 Single-lock anterior cervical plate and method - Patent 7,137,984 Single-lock anterior cervical plate and method - Patent 7,137,984
|
Anatomically contoured anterior cervical plates with bone ingrowth surfaces, providing for intersegmental compressive preloading, and a rigid and locked interface to all of the bone screws, with those engaging the vertebrae deployed in highly convergent pairs. The bone screws have a tapered self-tapping leading end, an increasing root diameter with a generally constant outer diameter with a thread that is narrow and sharp throughout and an enlarged head portion capable of an interference fit to the receiving holes of the plate. Instrumentation consists of plate holders, a compression apparatus and a pilot hole forming device that interlocks with the plate. Methods for spinal compression and bone hole preparation are provided.
|
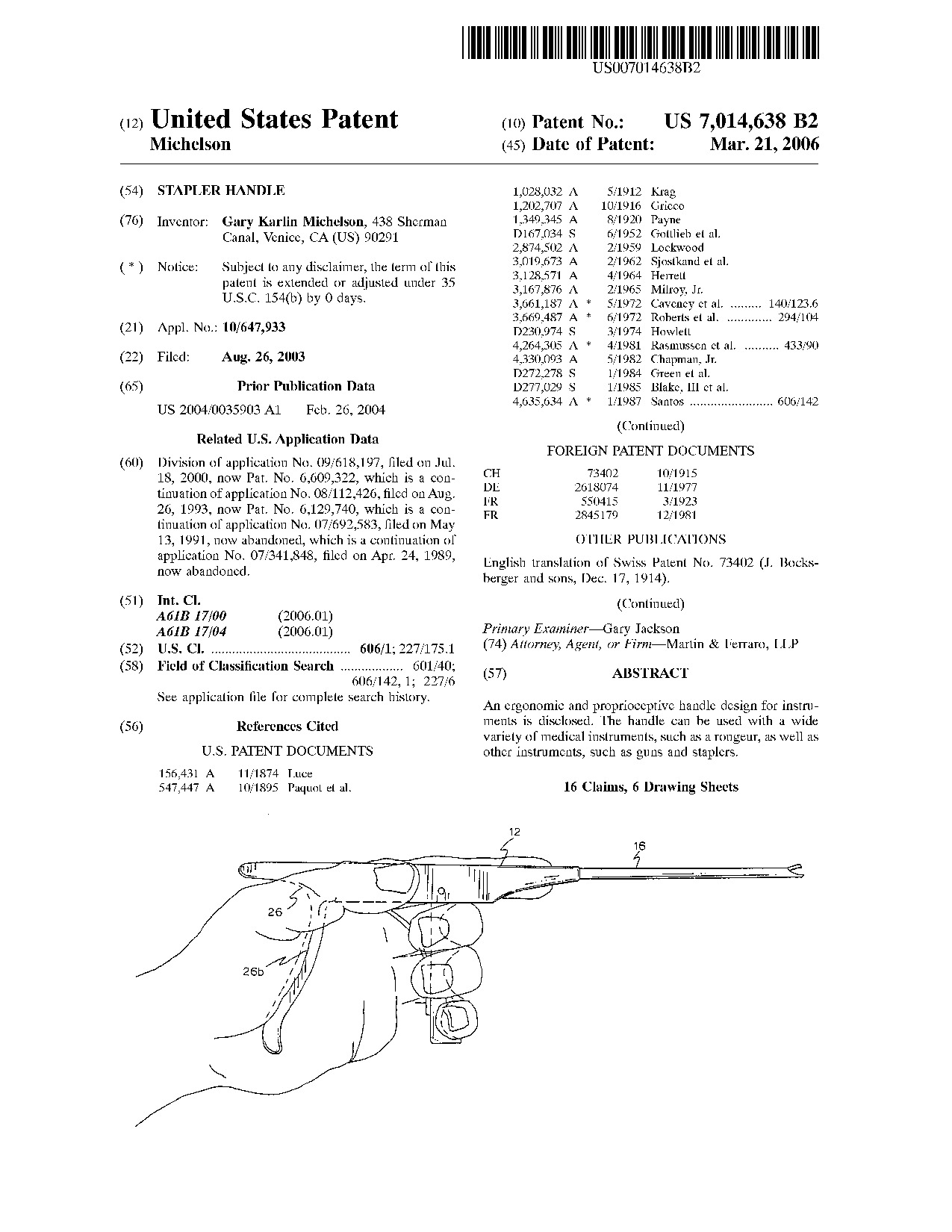 Stapler handle - Patent 7,014,638 Stapler handle - Patent 7,014,638
|
An ergonomic and proprioceptive handle design for instruments is disclosed. The handle can be used with a wide variety of medical instruments, such as a rongeur, as well as other instruments, such as guns and staplers.
|
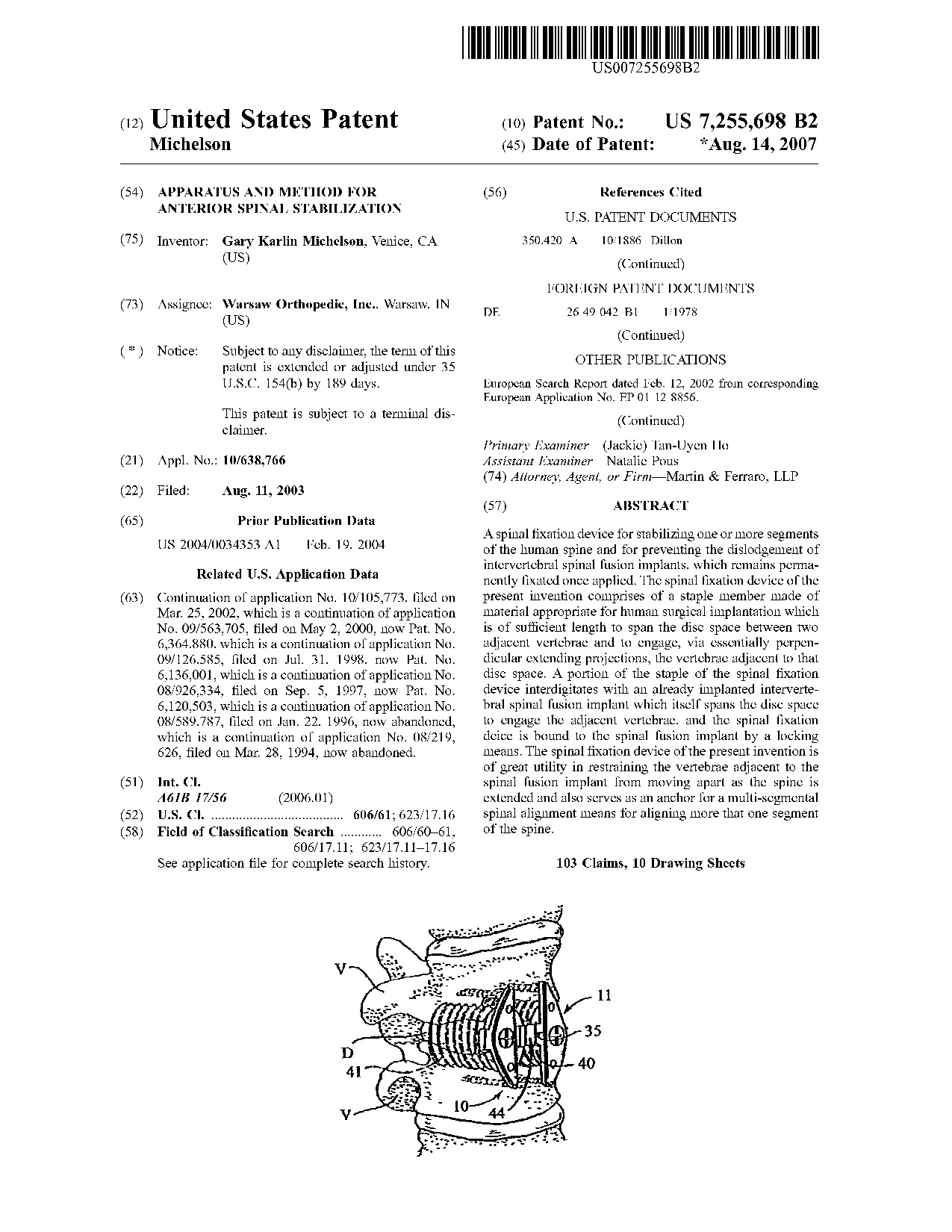 Apparatus and method for anterior spinal stabilization - Patent 7,255,698 Apparatus and method for anterior spinal stabilization - Patent 7,255,698
|
A spinal fixation device for stabilizing one or more segments of the human spine and for preventing the dislodgement of intervertebral spinal fusion implants, which remains permanently fixated once applied. The spinal fixation device of the present invention comprises of a staple member made of material appropriate for human surgical implantation which is of sufficient length to span the disc space between two adjacent vertebrae and to engage, via essentially perpendicular extending projections, the vertebrae adjacent to that disc space. A portion of the staple of the spinal fixation device interdigitates with an already implanted intervertebral spinal fusion implant which itself spans the disc space to engage the adjacent vertebrae, and the spinal fixation deice is bound to the spinal fusion implant by a locking means. The spinal fixation device of the present invention is of great utility in restraining the vertebrae adjacent to the spinal fusion implant from moving apart as the spine is extended and also serves as an anchor for a multi-segmental spinal alignment means for aligning more that one segment of the spine.
|
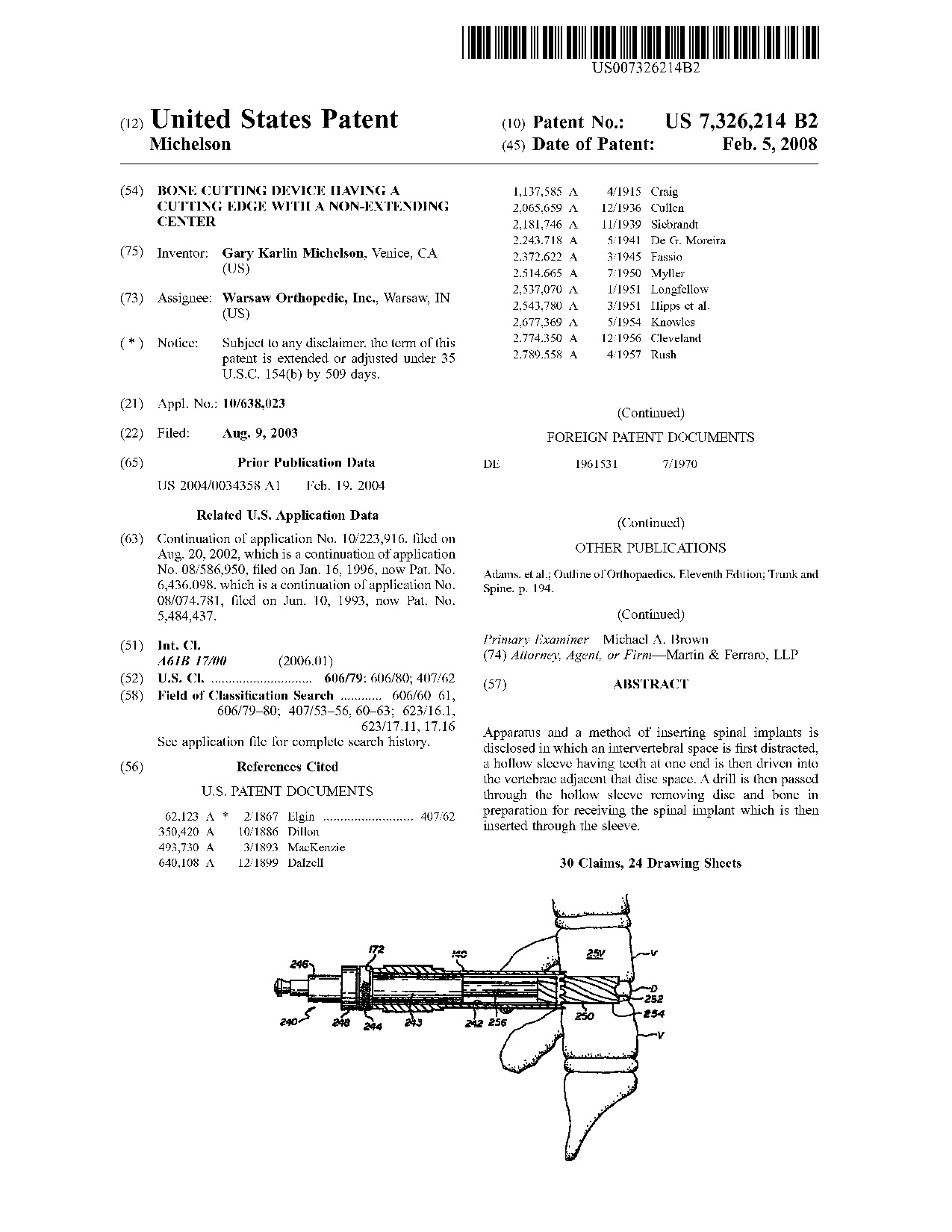 Bone cutting device having a cutting edge with a non-extending center - Patent 7,326,214 Bone cutting device having a cutting edge with a non-extending center - Patent 7,326,214
|
Apparatus and a method of inserting spinal implants is disclosed in which an intervertebral space is first distracted, a hollow sleeve having teeth at one end is then driven into the vertebrae adjacent that disc space. A drill is then passed through the hollow sleeve removing disc and bone in preparation for receiving the spinal implant which is then inserted through the sleeve.
|
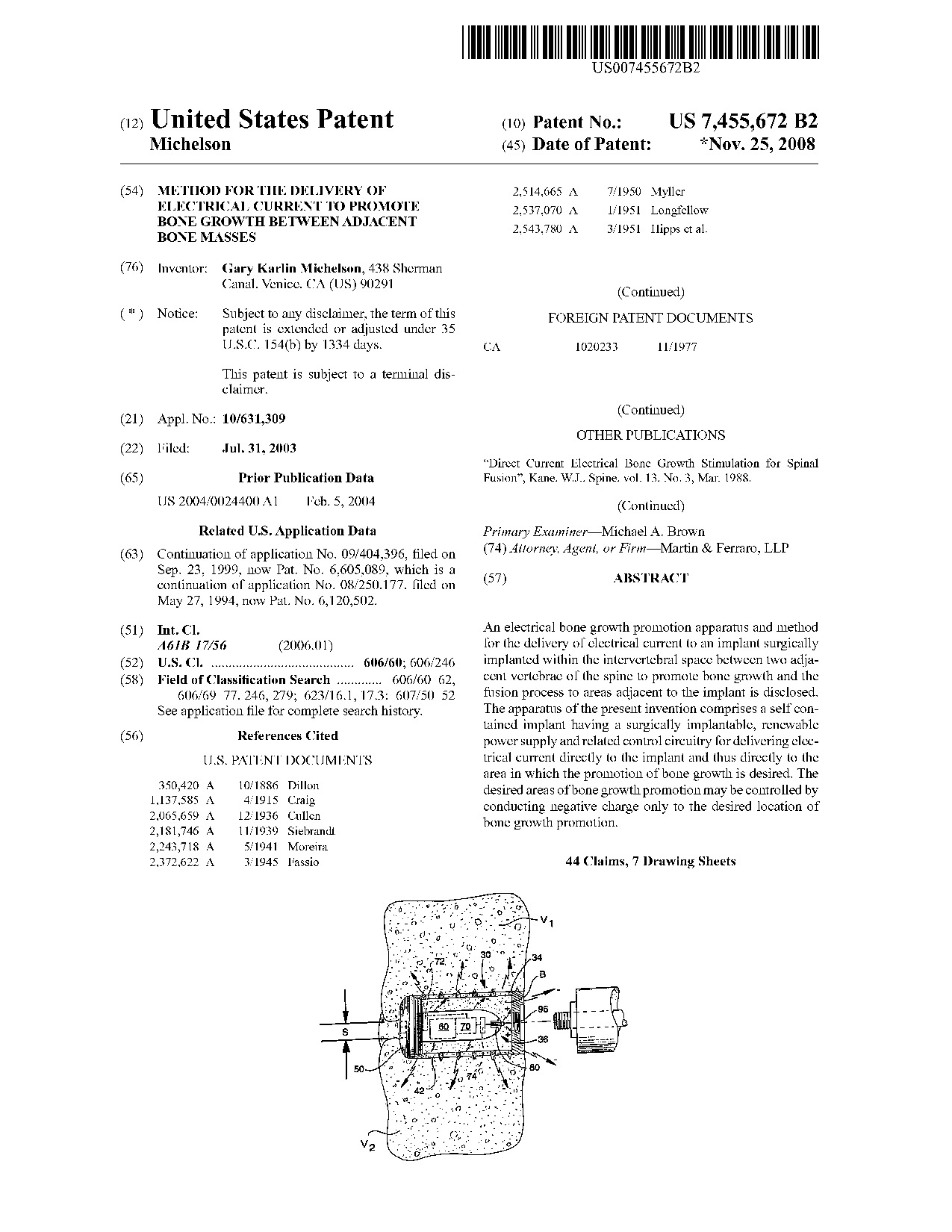 Method for the delivery of electrical current to promote bone growth between adjacent bone masses - Patent 7,455,672 Method for the delivery of electrical current to promote bone growth between adjacent bone masses - Patent 7,455,672
|
An electrical bone growth promotion apparatus and method for the delivery of electrical current to an implant surgically implanted within the intervertebral space between two adjacent vertebrae of the spine to promote bone growth and the fusion process to areas adjacent to the implant is disclosed. The apparatus of the present invention comprises a self contained implant having a surgically implantable, renewable power supply and related control circuitry for delivering electrical current directly to the implant and thus directly to the area in which the promotion of bone growth is desired. The desired areas of bone growth promotion may be controlled by conducting negative charge only to the desired location of bone growth promotion.
|
 Predictive toxicology for biological systems - Patent 7,853,406 Predictive toxicology for biological systems - Patent 7,853,406
|
Methods and apparatus to identify a potential toxicity of a therapy in a biological system are described. In one embodiment, a method uses a computer model that represents a set of biological processes of the biological system. The method includes executing the computer model to identify a first set of biological processes contributing to the occurrence of a toxic state of the biological system. The method also includes identifying a set of biological assays based on the first set of biological processes and testing the therapy in the set of biological assays to identify a second set of biological processes modified by the therapy. The method further includes identifying the potential toxicity of the therapy based on the second set of biological processes.
|
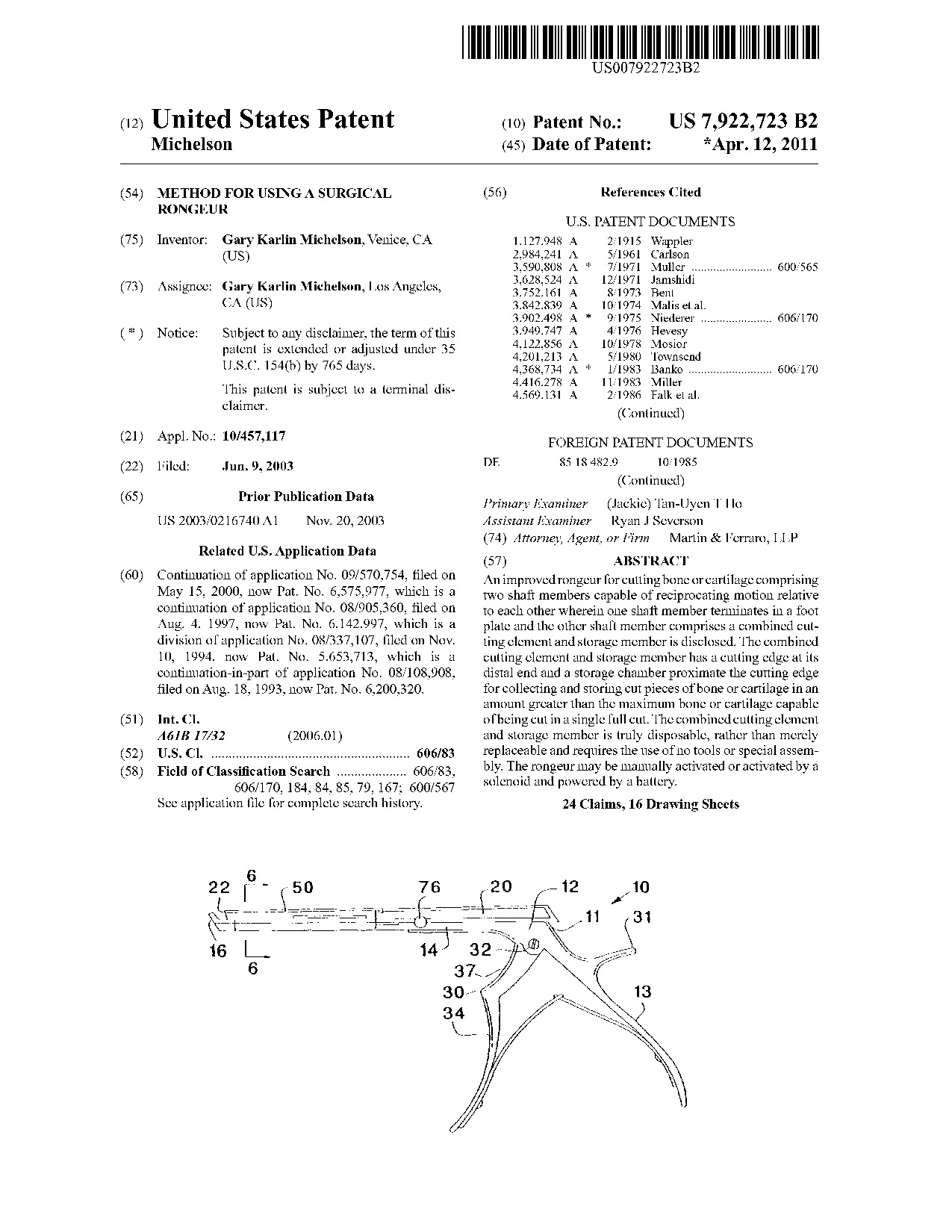 Method for using a surgical rongeur - Patent 7,922,723 Method for using a surgical rongeur - Patent 7,922,723
|
An improved rongeur for cutting bone or cartilage comprising two shaft members capable of reciprocating motion relative to each other wherein one shaft member terminates in a foot plate and the other shaft member comprises a combined cutting element and storage member is disclosed. The combined cutting element and storage member has a cutting edge at its distal end and a storage chamber proximate the cutting edge for collecting and storing cut pieces of bone or cartilage in an amount greater than the maximum bone or cartilage capable of being cut in a single full cut. The combined cutting element and storage member is truly disposable, rather than merely replaceable and requires the use of no tools or special assembly. The rongeur may be manually activated or activated by a solenoid and powered by a battery.
|
 Interbody spinal fusion implants with end cap for locking vertebral body penetrating members - Patent 7,033,394 Interbody spinal fusion implants with end cap for locking vertebral body penetrating members - Patent 7,033,394
|
An apparatus including an interbody spinal fusion implant having a leading end, a trailing end, and a length therebetween, and opposed upper and lower portions adapted to contact each of the adjacent vertebral bodies. Each of the upper and lower portions having at least one opening adapted to communicate with one each of the adjacent vertebral bodies and to communicate with one another to permit for the growth of bone from vertebral body to adjacent vertebral body through the implant. Each of the upper and lower portions has at least one screw hole passing therethrough proximate the trailing end. The apparatus further includes bone screws adapted for placement through the screw holes of the upper and lower portions and into each of the adjacent vertebral bodies adjacent the disc space to be fused and into which the implant is adapted to be positioned. At least one lock may be used to prevent the bone screws from backing out of the vertebral bodies and implant.
|
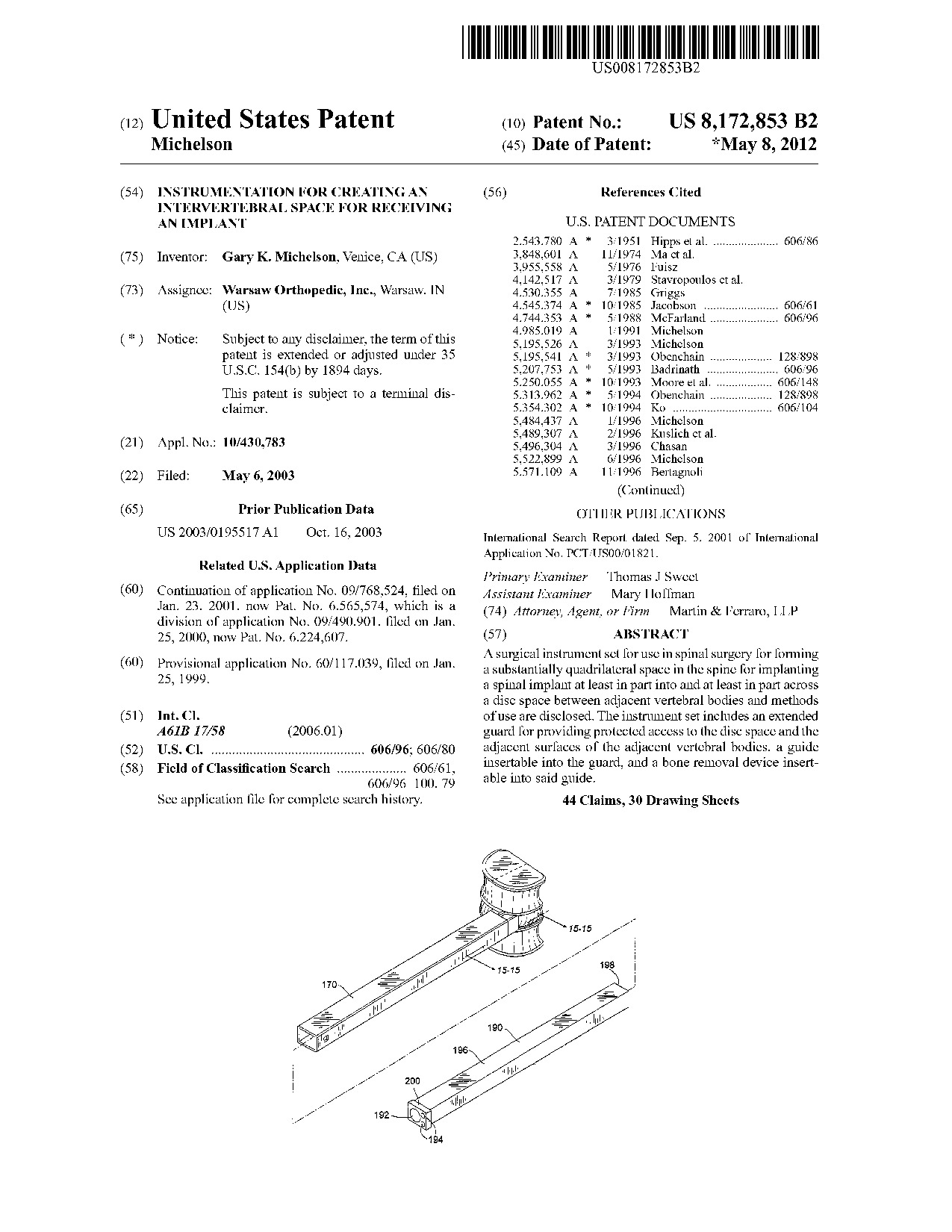 Instrumentation for creating an intervertebral space for receiving an implant - Patent 8,172,853 Instrumentation for creating an intervertebral space for receiving an implant - Patent 8,172,853
|
A surgical instrument set for use in spinal surgery for forming a substantially quadrilateral space in the spine for implanting a spinal implant at least in part into and at least in part across a disc space between adjacent vertebral bodies and methods of use are disclosed. The instrument set includes an extended guard for providing protected access to the disc space and the adjacent surfaces of the adjacent vertebral bodies, a guide insertable into the guard, and a bone removal device insertable into said guide.
|
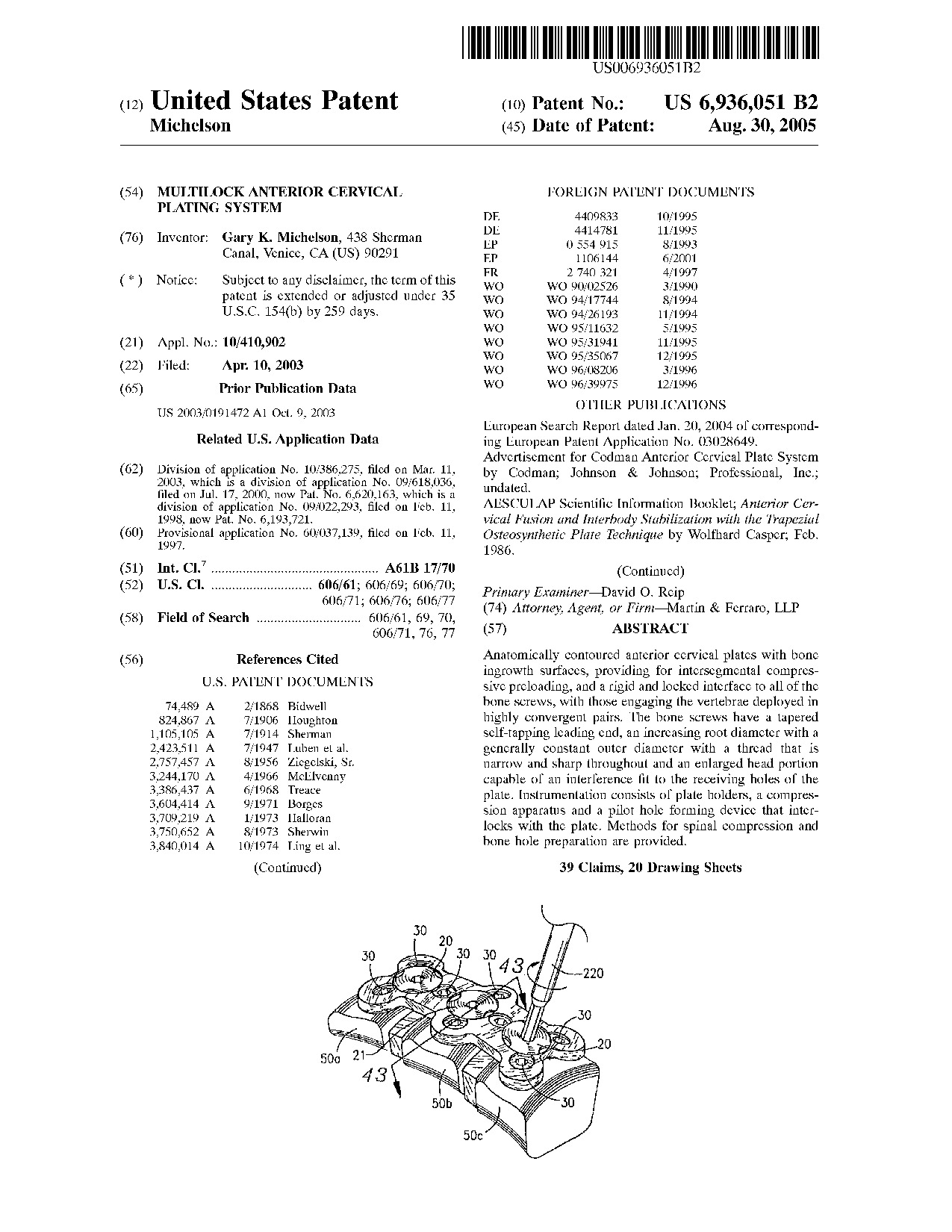 Multilock anterior cervical plating system - Patent 6,936,051 Multilock anterior cervical plating system - Patent 6,936,051
|
Anatomically contoured anterior cervical plates with bone ingrowth surfaces, providing for intersegmental compressive preloading, and a rigid and locked interface to all of the bone screws, with those engaging the vertebrae deployed in highly convergent pairs. The bone screws have a tapered self-tapping leading end, an increasing root diameter with a generally constant outer diameter with a thread that is narrow and sharp throughout and an enlarged head portion capable of an interference fit to the receiving holes of the plate. Instrumentation consists of plate holders, a compression apparatus and a pilot hole forming device that interlocks with the plate. Methods for spinal compression and bone hole preparation are provided.
|
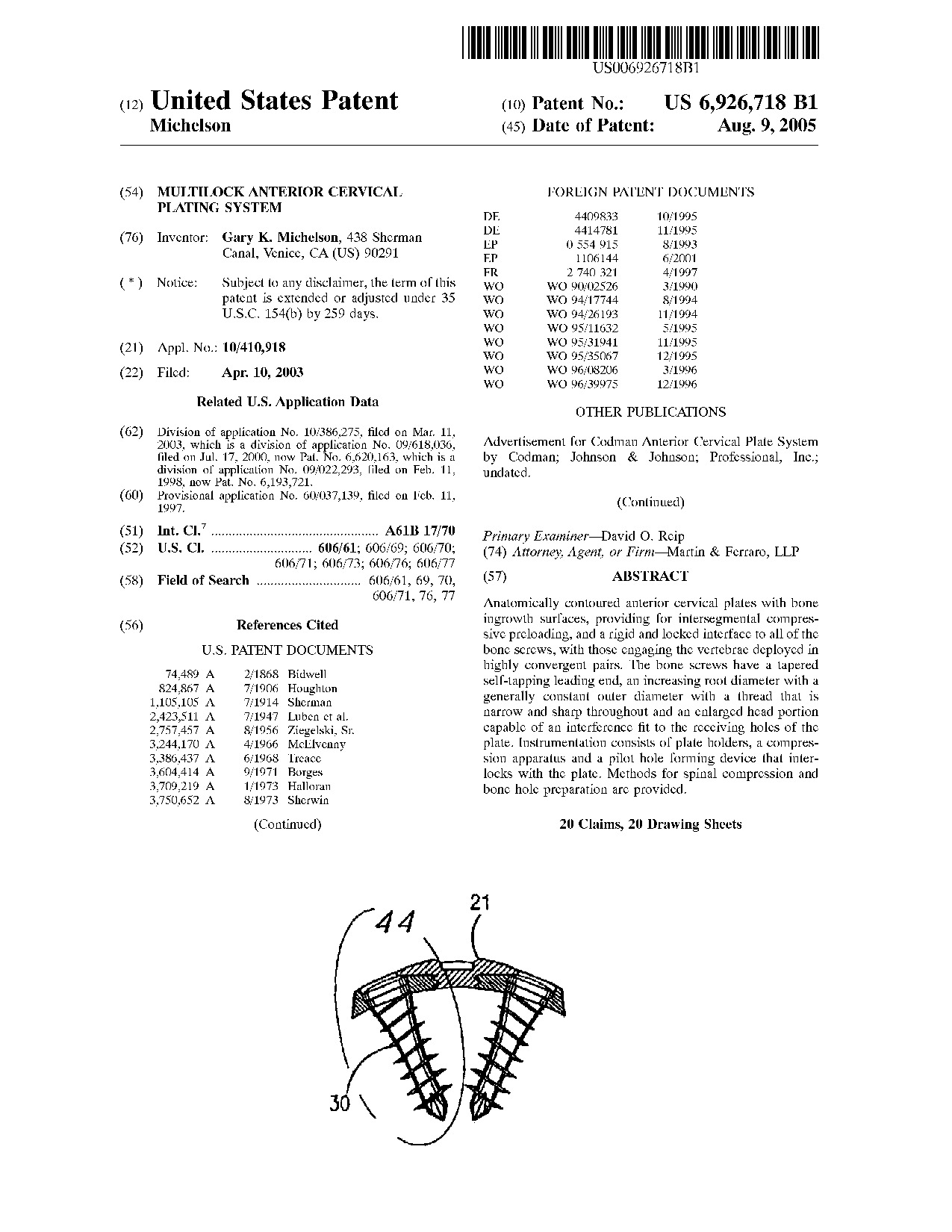 Multilock anterior cervical plating system - Patent 6,926,718 Multilock anterior cervical plating system - Patent 6,926,718
|
Anatomically contoured anterior cervical plates with bone ingrowth surfaces, providing for intersegmental compressive preloading, and a rigid and locked interface to all of the bone screws, with those engaging the vertebrae deployed in highly convergent pairs. The bone screws have a tapered self-tapping leading end, an increasing root diameter with a generally constant outer diameter with a thread that is narrow and sharp throughout and an enlarged head portion capable of an interference fit to the receiving holes of the plate. Instrumentation consists of plate holders, a compression apparatus and a pilot hole forming device that interlocks with the plate. Methods for spinal compression and bone hole preparation are provided.
|
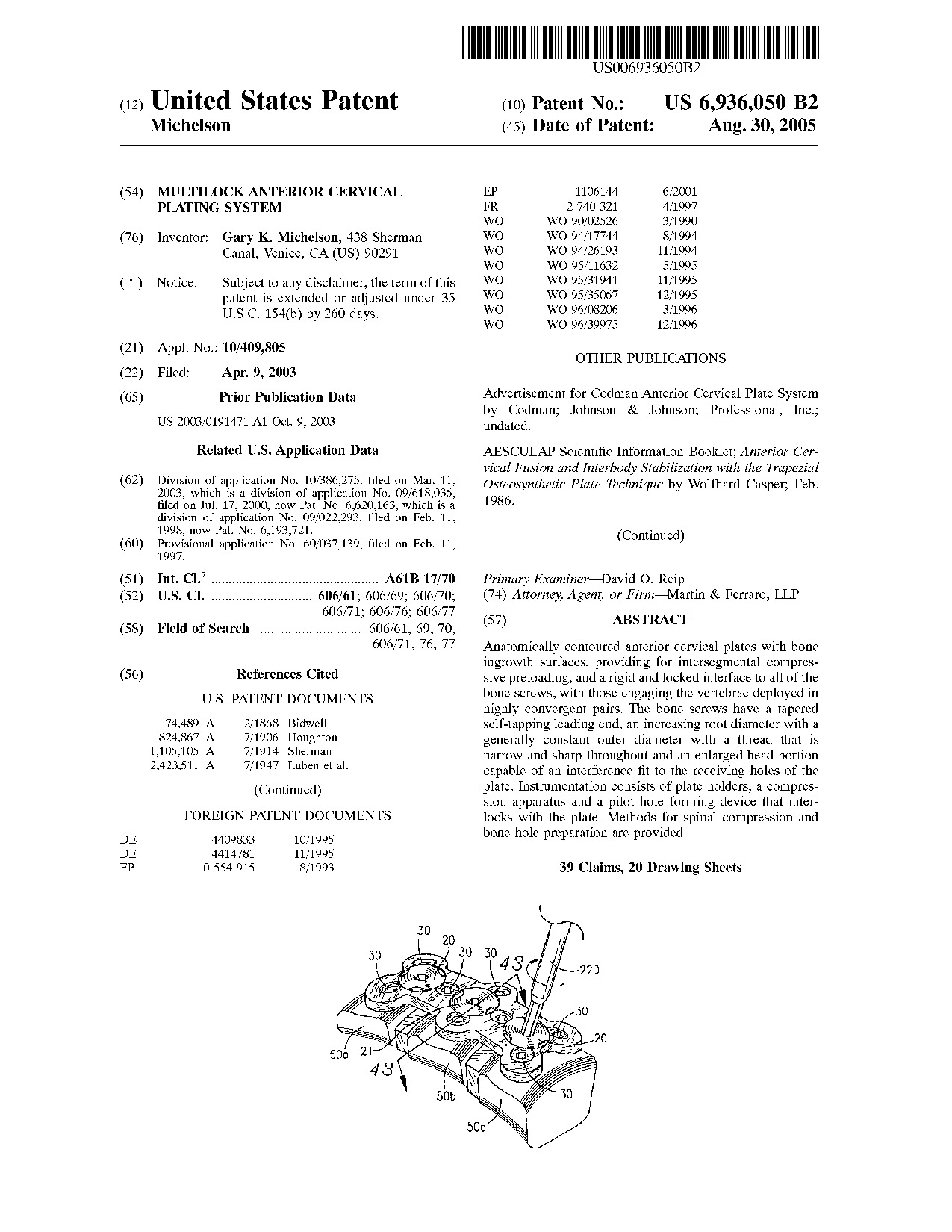 Multilock anterior cervical plating system - Patent 6,936,050 Multilock anterior cervical plating system - Patent 6,936,050
|
Anatomically contoured anterior cervical plates with bone ingrowth surfaces, providing for intersegmental compressive preloading, and a rigid and locked interface to all of the bone screws, with those engaging the vertebrae deployed in highly convergent pairs. The bone screws have a tapered self-tapping leading end, an increasing root diameter with a generally constant outer diameter with a thread that is narrow and sharp throughout and an enlarged head portion capable of an interference fit to the receiving holes of the plate. Instrumentation consists of plate holders, a compression apparatus and a pilot hole forming device that interlocks with the plate. Methods for spinal compression and bone hole preparation are provided.
|
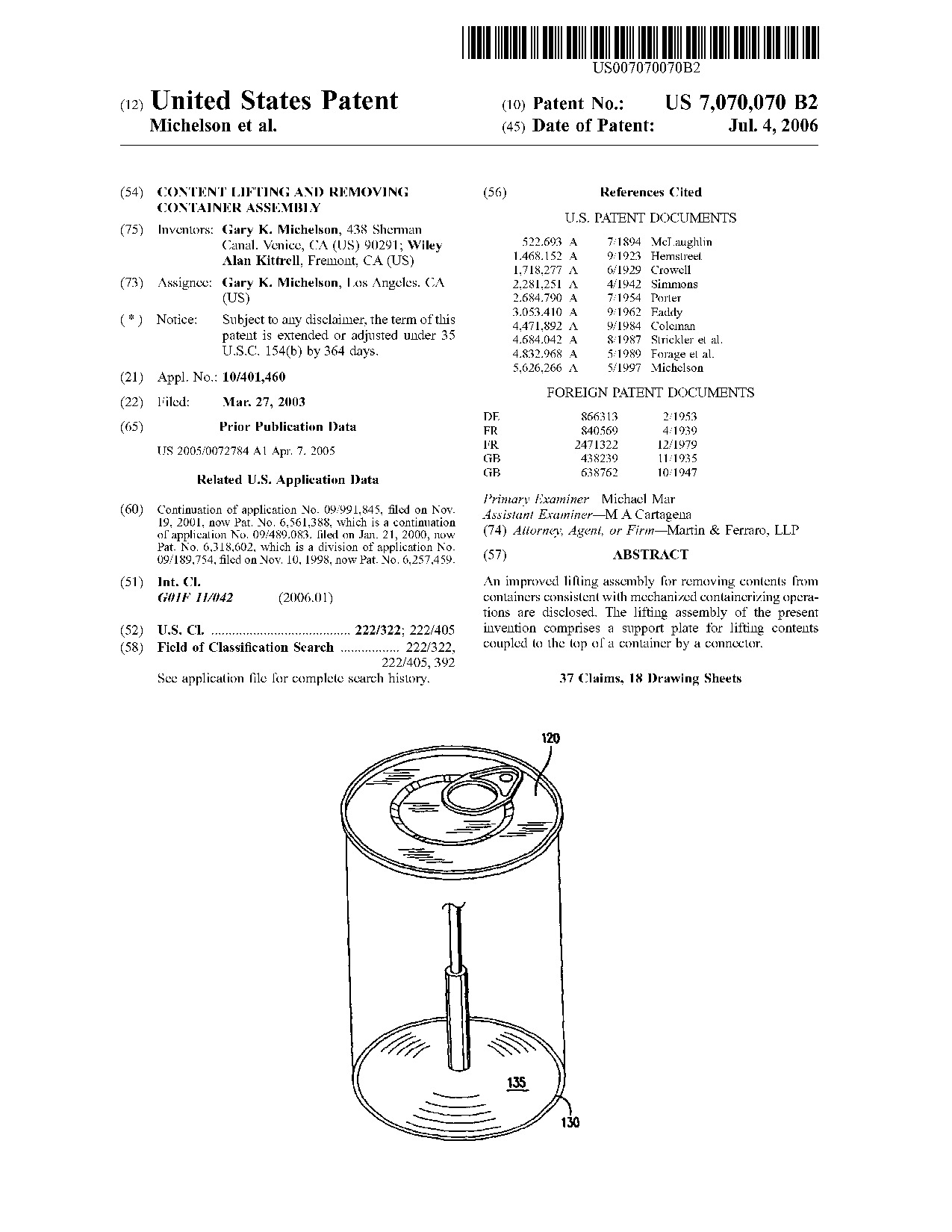 Content lifting and removing container assembly - Patent 7,070,070 Content lifting and removing container assembly - Patent 7,070,070
|
An improved lifting assembly for removing contents from containers consistent with mechanized containerizing operations are disclosed. The lifting assembly of the present invention comprises a support plate for lifting contents coupled to the top of a container by a connector.
|
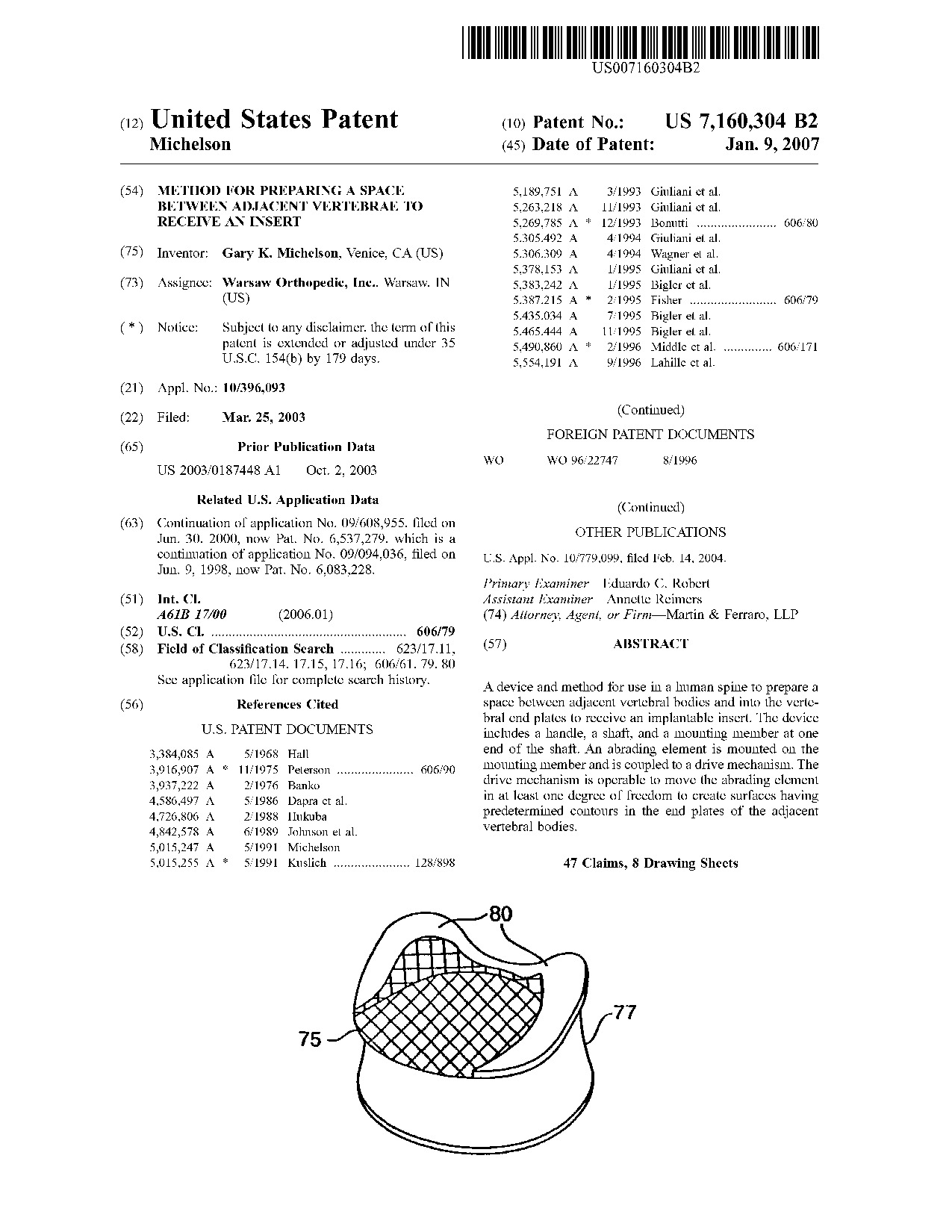 Method for preparing a space between adjacent vertebrae to receive an insert - Patent 7,160,304 Method for preparing a space between adjacent vertebrae to receive an insert - Patent 7,160,304
|
A device and method for use in a human spine to prepare a space between adjacent vertebral bodies and into the vertebral end plates to receive an implantable insert. The device includes a handle, a shaft, and a mounting member at one end of the shaft. An abrading element is mounted on the mounting member and is coupled to a drive mechanism. The drive mechanism is operable to move the abrading element in at least one degree of freedom to create surfaces having predetermined contours in the end plates of the adjacent vertebral bodies.
|
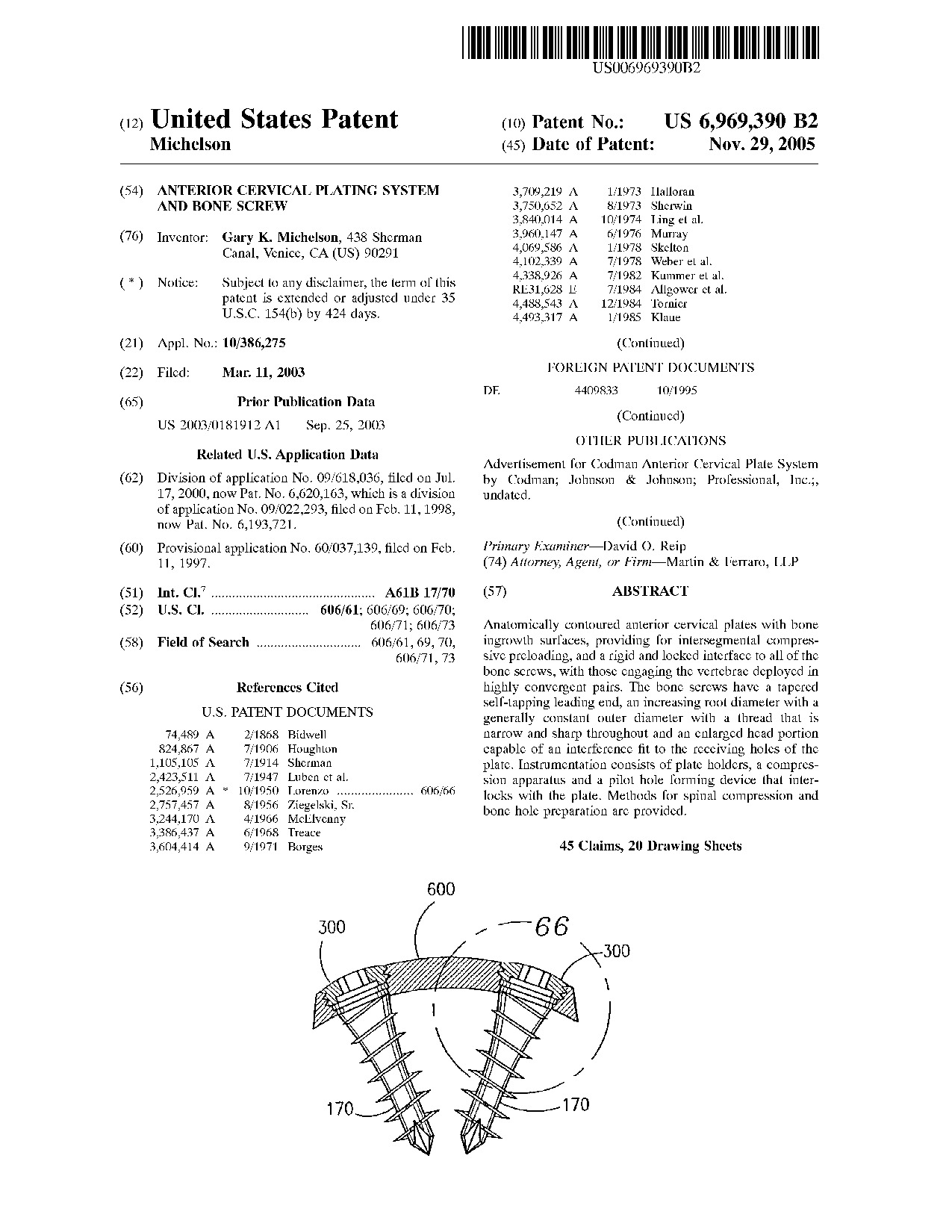 Anterior cervical plating system and bone screw - Patent 6,969,390 Anterior cervical plating system and bone screw - Patent 6,969,390
|
Anatomically contoured anterior cervical plates with bone ingrowth surfaces, providing for intersegmental compressive preloading, and a rigid and locked interface to all of the bone screws, with those engaging the vertebrae deployed in highly convergent pairs. The bone screws have a tapered self-tapping leading end, an increasing root diameter with a generally constant outer diameter with a thread that is narrow and sharp throughout and an enlarged head portion capable of an interference fit to the receiving holes of the plate. Instrumentation consists of plate holders, a compression apparatus and a pilot hole forming device that interlocks with the plate. Methods for spinal compression and bone hole preparation are provided.
|
 Self-broaching, rotatable, push-in interbody spinal fusion implant and method for deployment thereof - Patent 7,056,342 Self-broaching, rotatable, push-in interbody spinal fusion implant and method for deployment thereof - Patent 7,056,342
|
An interbody spinal fusion implant for insertion across a disc space between adjacent vertebral bodies of a human spine has a body two top side and two bottom side junctions, with at least a pair of diagonally opposed junctions having a distance therebetween that does not significantly exceed the implant body height. The implant also includes one or more bone penetrating protrusions extending outwardly from at least the upper and lower walls of the implant. The implant is inserted on its side between adjacent vertebral bodies and then rotated 90 degrees into place. The protrusions penetrate the endplates upon rotation, thereby securing the implant within the spine. The implant has at least one passage therethrough from the upper wall to the lower wall to promote fusion through the implant. Because of the specialized opposed junctions overdistraction between the adjacent vertebral bodies is avoided when the implant is rotated from an initial insertion position to a final deployed position. In one suggested implant set, two implants are rotated in opposite directions into their respective final deployed positions, and a third specialized implant is positioned therebetween to lock the three implants together along cooperating surfaces. A method for deploying the push-in implants is also disclosed.
|
